The wastewater treatment plant can be described as a facility that combines various processes such as chemical, physical, and biological for the treatment of industrial wastewater and removing pollutants from it.
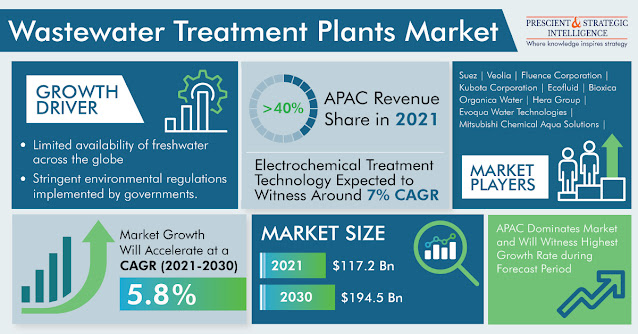
The wastewater treatment industry generates $117.2 billion revenue in 2021, and it is projected to rise to $194.5 billion in 2030, advancing at a rate of 5.8% in the coming years. It is due to the limited availability of fresh water and its worldwide increasing usage, accounting for six times rise over the last century.
Physical Waste Water Treatment
The foremost step in the treatment of industrial and sanitary effluents is the physical wastewater treatment. It prevents damage to equipment used in biological and chemical treatment. The physical wastewater treatment equipment and processes vary depending on the affluents type and desired quality of the wastewater. The wastewaters are very colored and have high biological and chemical oxygen contents. They possess high electrical conductivity and are chemically alkaline in nature.
Physical wastewater treatment is a separation process of particulate matter and solids in sanitary and industrial effluents known as physical purification. It might include fabric pieces, tree foliage, plastic, and sand parts, depending on the type of sewage. The failure in removing these particles causes a lot of pressure on the equipment and impacts the quality of the chemical and biological wastewater treatment. Therefore, industrial wastewater treatment is increasingly implemented.
Various parameters impact the wastewater treatment method cost. Factors such as pollutants type, wastewater chemical composition, chemicals cost, operating cost, and treatment process generated waste collection cost affects the wastewater treatment method selection.
Biological Wastewater Treatment
Biological wastewater treatment involves natural processes to support the decomposition of organic substances. This treatment method relies on bacteria, nematodes, or other microorganisms for breaking down organic wastes utilizing the normal cellular processes. Wastewater usually includes a buffet of organic matter, such as wastes, garbage, and partially digested foods. It includes the contents of heavy metals, toxins, and pathogenic organisms.
The aim of biological wastewater treatment is to develop a system that facilitates the easy collection of the results of the decomposition and ensures their proper disposal. This treatment is used worldwide due to its effectiveness and economical cost over mechanical and chemical processes.
Chemical Wastewater Treatment
There are various types of chemical wastewater treatment methods such as mining, industrial, and other sectors, such as neutralization, chlorination, coagulation, adsorption, and ion exchange. Most such treatment methods utilize the oxidation process for the purification of wastewater. The highly effective chlorine-based oxidation is the widely adopted oxidation technique.
The shift toward the adoption of safer and more effective oxidation techniques involves the usage of hydrogen peroxide, ultraviolet light, and ozone as oxidizing agents to mitigate unwanted contaminants and disinfects in the treated water without any risks of chlorine usage.
Neutralization- Chemical Wastewater Treatment
The neutralization process involves the addition of acid or base to the water to neutralize the pH value, the iron and other polyvalent metals are highly used as coagulations in the coagulation process. This process is also utilized for separation of suspended solids from the contaminated water. According to Minnesota Rural Water Association, the selection of coagulant chemicals relies on the type of suspended solid, including other factors such as facility design, and raw water conditions.
Electrochemical Wastewater Treatment
There are numerous processes of electrochemical wastewater treatment. For instance, sewage purification involves clarification, phosphate removal, and disinfection to reduce costs as compared to the traditional processes. The electrochemical treatment process is highly efficient and minimizes the process detention time.
Mostly electrochemical water treatment methods involve electricity usage as a primary reactant for conducting the treatment process. It includes electrocoagulation, electrodialysis, electro floatation, and electrochemical oxidation.
Therefore, the wastewater treatment processes are highly utilized in various sectors such as mining, industrial, and others for disposal of wastes, and purifying the water by removing contaminants and neutralizing the pH level to make it safe for further usage.